Centrifugation is a method that incorporates the separation of varying components in a solution using centrifugal force.
The acceleration applied triggers the movement of denser molecules in the direction of the periphery.
Besides, the molecules with lesser density are subjected to move in the path towards the center.
Centrifuges and their types have been the subject of research and study for various industries dealing in laboratory-related work. Despite their multiple variations, the core of all the devices is sedimentation.
The centrifuges use this principle to perform the process of separation. A centrifuge to separate mixtures is subject to speed, industry use and certain other factors.
All these factors create distinction in the types of centrifuges used for the purpose.

Varying Types of Centrifugation
Before moving towards different types of centrifuges, let’s understand the slight variation in the concepts or application methods of centrifugation.
1, Preparative Centrifugation: The preparative centrifugation technique aims to perform separation, isolation, and purification of several cellular constituents required for biochemical investigations.
It’s aligned with the process of cell centrifugation as a massive volume of cellular components is needed to be isolated to perform the studies about morphology, biological activities and other composition.
A preparative centrifugation process is applicable when separating the entire plasma membrane, cell, chromatin, viruses, lipoproteins and nucleic acids are required.
2, Analytical Centrifugation: Analytical centrifugation is a technique applied to comprehend the macromolecules and pure compounds to examine the molecular weight, shape and purity of the specific compound.
It is majorly associated with the study of sedimentation features present in the biological macromolecules compared to fractions.
Preparative and analytical centrifugation differs majorly on these factors as the former works with particles, and the latter is about pure macromolecules.
There is another difference in analytical and preparative centrifugation following the size of the sample.
The analytical method requires a smaller sample size and a specific centrifuge tool, and a detector system for monitoring.
3, Differential Centrifugation: The process of differential centrifugation aligns with the separation of several elements as per the size of the particles.
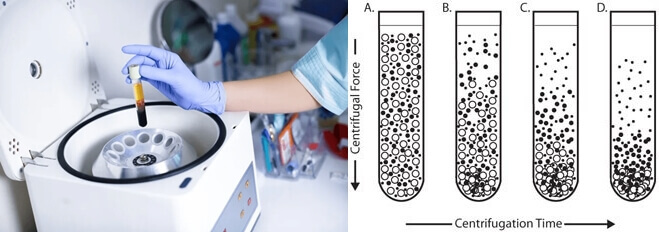
This method is majorly applicable in the simple pelleting process and the process of obtaining partly pure preparation associated with subcellular macromolecules and subcellular organelles.
The process of differential velocity centrifugation uses the rate of sedimentation to separate particles into several groups.
4, Density Gradient Centrifugation: Density Gradient Centrifugation can be a technique that reflects the purification of subcellular organelles and macromolecules that persist in varying sizes densities.
The process involves creating density gradients via a gradient media layer placed on top of another layer.
For instance, the sucrose present in a tube persisting the heaviest layer is placed at the bottom, and the lightest layer is positioned at the top. The mode of placement could be continuous or discontinuous.
Later, the centrifuge machine is activated. There are several types of density gradient centrifugation. These include rate zonal and isopycnic centrifugation, which are the main ones.
The rate zonal density gradient centrifugation technique is one of the most applied in the separating particles as per significant size differences.
Others include the final density gradient centrifugation method, CSCL density gradient centrifugation, equilibrium density gradient centrifugation, among other density gradient centrifugation types.
What Are The Types Of Centrifuges?
There are different types of centrifuges, which are used for varying purposes. The use of different kinds of filtration centrifuge depends on the industry and the subject matter.
In simple terms, a centrifuge is used for the separation of particles from their solutions. Take a look at numerous variants of centrifuges.
1, Industrial Centrifuge
As the name suggests, an industrial centrifuge is used in chemical and other industries. These industries include pharmaceutical, biotechnology, chemical and food processing industries as they have to deal with several heterogeneous mixtures.
Centrifuge machines in the pharmaceutical industry are of utmost demand as the work aligns with extensive laboratory work.
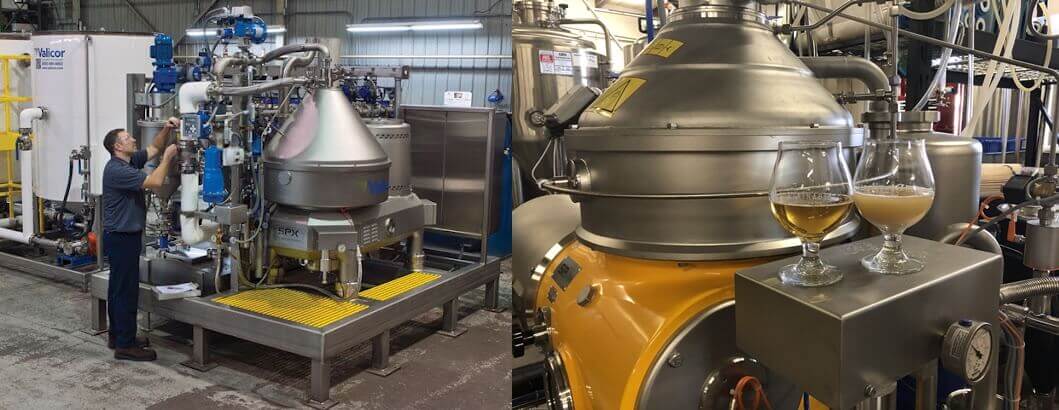

■ What Is An Industrial Centrifuge?
An industrial centrifuge has a critical role in the production of several things at once.
Most common usage, other than the pharmaceutical centrifuge, is aligned in the agriculture and food industry. Centrifugation in food processing is observed in the dairy sector as well.
Centrifugation helps to reduce the environmental impact in the case of chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The separation of elements and particles is equally crucial as their combining step.
To obtain pure reactants, it is essential to undergo a centrifugation process to separate several aspects. A centrifuge device aims to distinguish the heterogeneous mixtures with the use of their density.
■ Industrial Centrifuge Working Principle
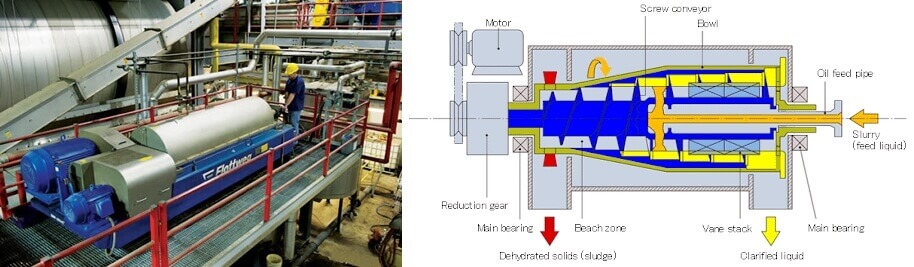
The principle applied to several types of industrial centrifuge devices is the application of centrifugal force.
It uses high-speed rotations that align with an extensive range of revolutions within a minute to generate a higher centrifugal force that suffices the separation of liquids and solids in a few minutes.
2, Ultracentrifugation
Ultracentrifugation is a particular method applied to spin the molecules or given samples at an extremely high pace.
The existing model of ultracentrifuge machine can spin at a speed of 150,000 rotations in a minute. It equals 1,000,000 g.
Though it’s quite useful, the extreme force could increase the temperature, further damaging the sample.

To avert this situation, the ultracentrifuge devices are facilitated with a set of vacuum systems that would manage its consistent temperature within its rotor.
Centrifuge and ultracentrifuge devices have a minimal variation that aligns with the level of speed.
■ Ultracentrifugation Principle
The principle in an application for ultracentrifugation is similar to that of standard centrifugation. It is the same as how a centrifuge separates the materials.
The method takes the density, size, viscosity of the particular solvent to divide them into their homogenous groups.
Take a look at the rules followed during ultracentrifugation:
- With a higher density, centrifugation works even faster in a centrifugal field.
- The size of the biological particle affects the speed as a massive matter would have a higher pace in the centrifugal field.
- The movement of a particle slowing down in the denser biological buffer system.
- The speed of the particle also reduces with a higher frictional coefficient. It associates with the friction within the neighboring environment and the component.
- A fast movement is observed when a greater centrifugal force is applied.
- The sedimentation rate in centrifugation will be nil if the density of the surrounding medium and the particle are equal.
■ Ultracentrifugation Definition
To comprehend ultracentrifugation decently, one could determine it as an advanced centrifuge machine that works at a very high speed to separate the small-sized molecules, which are not feasible to be separated from conventional centrifuge machines.
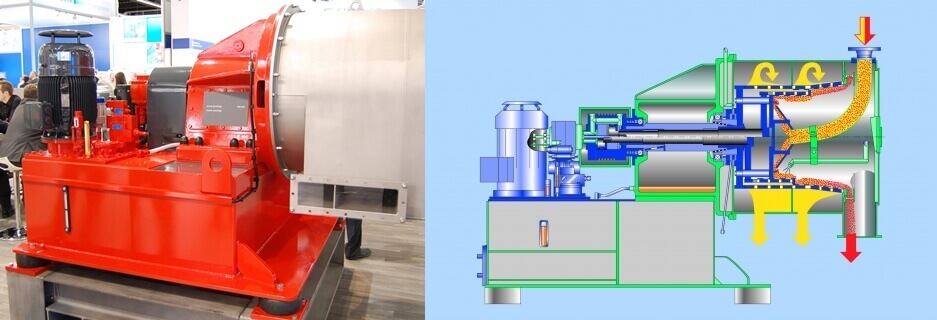
3, Pusher Centrifuge
Pusher centrifuge machine or horizontal centrifuge is one of the types of centrifuge machine used for continuous filtering in solid and liquid separation. It is highly used in the mineral and chemical industries.
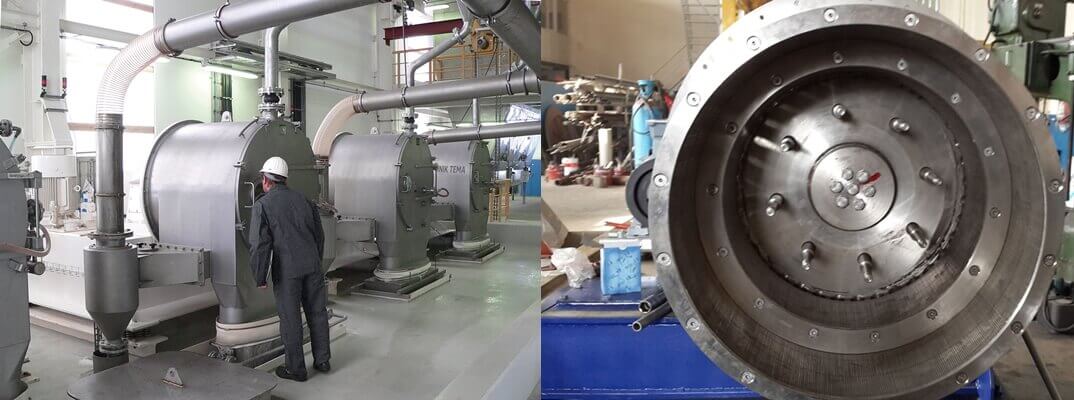

These pusher centrifuges have been in operation for over 60 years, especially in procedures like dewatering of comparatively large and free-draining crystals.
A pusher centrifuge manufacturer integrates a unique design that helps to reduce the level of impurity, moisture and breakage of crystals within a discharged cake.
■ Pusher Centrifuge Definition
Pusher centrifuges are popularly known as basket centrifuges that incorporate a filtration bowl.
These filtration bowls have metal screening sheets, with some having an option of slotted sieves. The ones with slotted sieves are also known as perforated basket centrifuges.
Pusher centrifuges have systems that filter the liquid present in the field to further retain the solids in the form of filter cakes.
It uses an oscillating pushing movement to transfer the cakes from the bowl. These systems are used to wash the solids as well.
The work of pusher centrifuges is continuous. Hence, it is a constant centrifuge machine that is used for large quantities of solids, where the requirement of residual moisture and purity is minimal or medium.
■ Pusher Centrifuge Working Principle
The pusher centrifuge is used to separate solids within the liquid solutions by applying the centrifugal force that moves or rotates on its horizontal axis.
A hydraulic system caters the power on the centrifugal piston to leave the discharged area with a separation of wet materials and their existing moisture.
A hydraulic mechanism enables the sedimentation of solids and liquid via the operating valve’s reciprocation that directs it towards the chamber of solid discharge.
4, Refrigerated Centrifuge
A refrigerated centrifuge is taken into applications where the subject requires consistent temperature. A refrigerated centrifuge machine applies a maximum speed while ensuring a suitable and compatible range of temperature.
It is a temperature-controlled centrifuge that provides a range of temperature within -20 degrees Celsius to – 40 degrees celsius.
With such a suitable range, refrigerated centrifuge machines are helpful for the analysis of PCR, RNA, DNA and other types of antibodies.
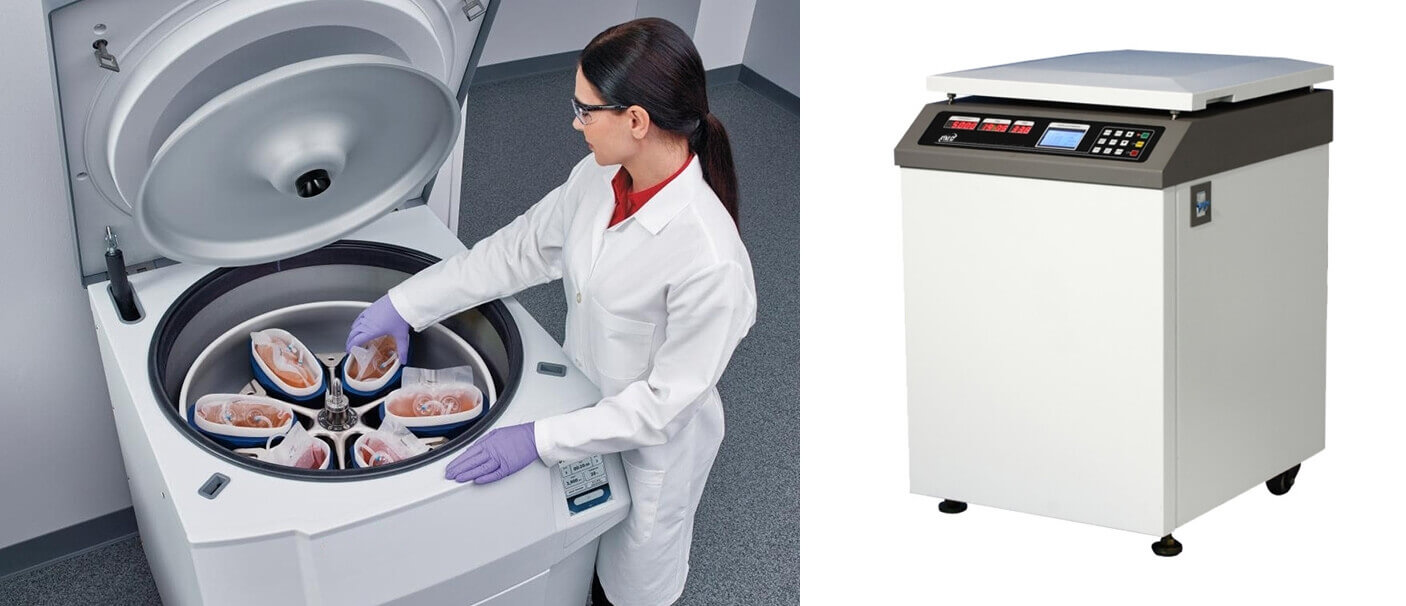

■ Refrigerated Centrifuge Definition
A refrigerated centrifuge can be referred to as a high-speed centrifuge that works well for medium-capacity requirements.
It enables molecular uses within tubes for 250 ml and further comes with options like fixed angle rotor and swing bucket rotor options.
There are specific options like large capacity refrigerated centrifuge with intense place capacity to increase versatility.
■ Refrigerated Centrifuge Principle
There are several types of centrifuges with temperature control aids. These are specially designed to maintain the low-temperature requirements in the centrifuges.
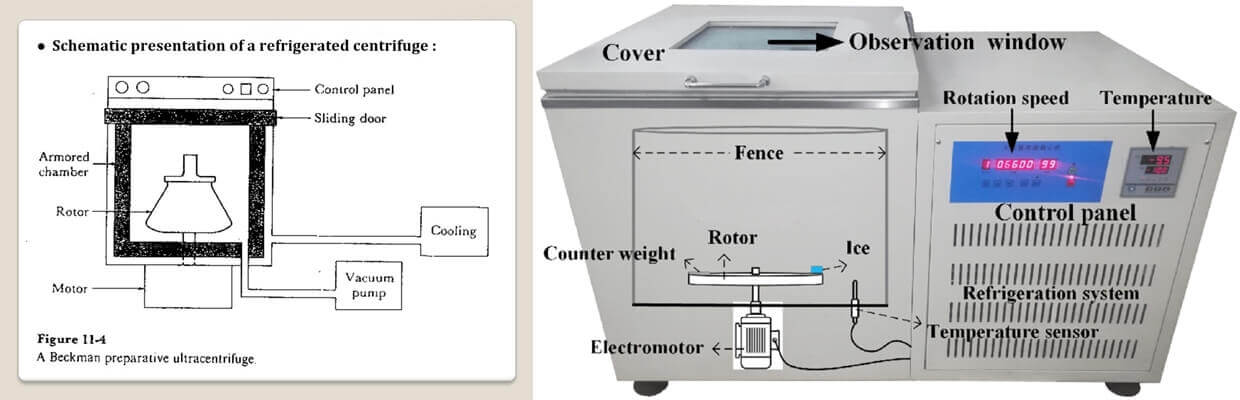
- Besides racks and rotors, refrigerated centrifuges also have a control unit to manage the temperature within the subject tubes.
- The high-speed refrigerated centrifuge offers an RCF capacity of around 60 000 g, making it ideal for the sedimentation of several biological molecules.
- Such centrifuges are purposely applied to collect substances, which have a rapid separation rate. For instance, it includes erythrocytes, yeast cells and chloroplasts etc.
- The refrigerated centrifuge chamber is perfectly sealed from the outer end to suit the desired temperature requirements.
5, Benchtop Centrifuge
Benchtop centrifuge is also known as tabletop centrifuge machine with lower throughputs. These centrifuge types are not capable of extending high-end g forces as compared with the floor-standing centrifuge models.
However, they still manage to work with several applications. The tabletop centrifuge models are used in clinical work that is related to diagnostics.
Other than this, high-speed instruments align with complete cell harvesting and specific other nucleic acid uses.
Such centrifuges are also known as nuclear centrifuge machines. Some other multi-purpose centrifuges also come into the category of benchtop centrifuges that persist either the fixed-angle rotor or swinging bucket rotor.
There are some benchtop centrifuges known as cell washers with the ability to wash the red blood cells.
■ Benchtop Centrifuge Definition
A benchtop microcentrifuge is one of the most crucial components of laboratory equipment.
It works on an electric motor and further implements a rotational motion on an object placed on the fixed axis that applies a perpendicular force on the axis.
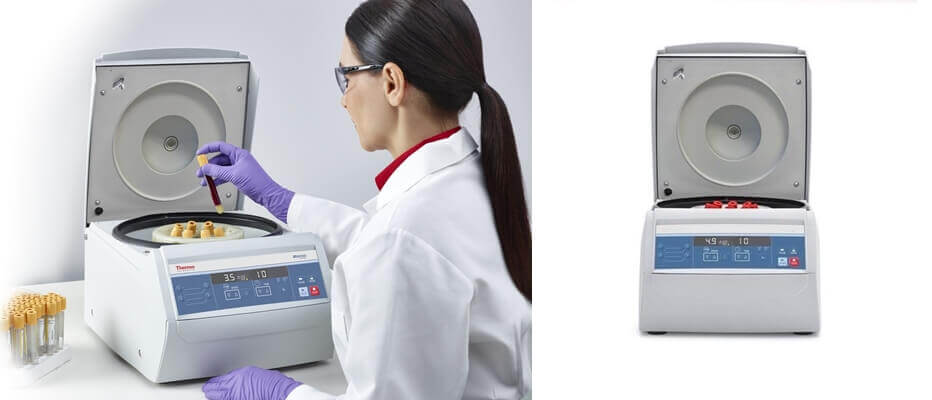

Centrifuges combine with refrigerated benchtop centrifuge to aid the perfect laboratory usage while enabling a small footprint. The laboratories having less space can work with these centrifuges to carry out their operations.
These compact centrifuges are taken into clinical laboratories as well as for research purposes. The application includes sedimentation, column chromatography and filtration.
■ Benchtop Centrifuge Principle
The benchtop centrifuge works on the same principle of sedimentation and centrifugal force as in other centrifuges. They are operated by an electric motor, which makes it an electric centrifuge machine.
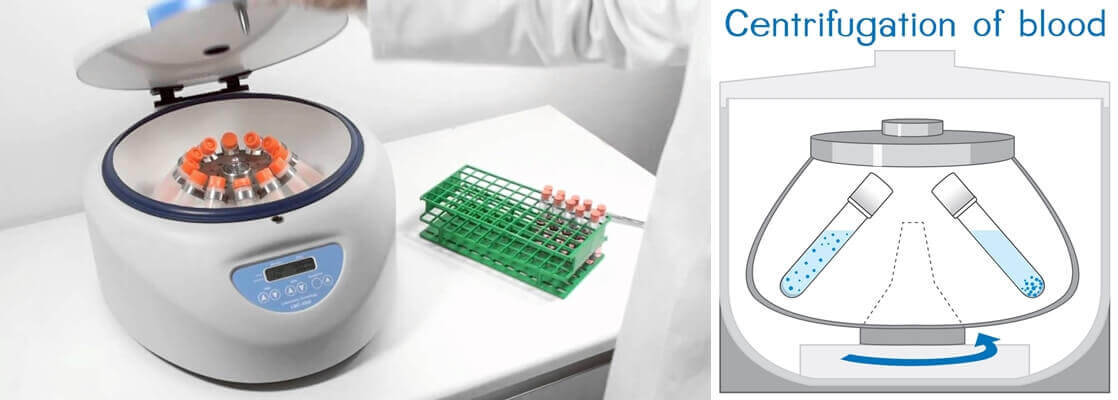
The machine rotates the tubes on a specific axis that further develops a perpendicular force. Several versions of benchtop centrifuge can be found in the market that suits a variety of purposes.
6, Hematocrit Centrifuge
A hematocrit centrifuge aligns for the specified purpose of blood centrifugation. Hematocrit is known as the composition of red blood cells within the complete volume of the blood.
Red blood cells are essential for an individual’s well-being and, hence, the blood’s subway system.
Centrifuge for hematocrit would help understand the accurate composition of the red blood cells in an individual body.
■ What Is A Hematocrit Centrifuge?
Hematocrit centrifugation aligns with a similar principle as found in centrifuge machines for the laboratory. Although, the size of the samples is tiny. Hematocrit centrifuge rpm has a range of 7000 to 15000.

A hematocrit centrifuge can hold over 24 capillary tubes with a specific size of 1.2mm x 75mm. Micro hematocrit centrifuge works with a tube that is equipped with anticoagulated whole blood. One of the ends of the tubes is secured with insertion or heat via a sealing clay for centrifugation.
The areas where microhematocrit is observed are biochemistry, blood separation, microbic immunity genetics, and more.
■ Hematocrit Centrifuge Definition
In simple terms, the definition of hematocrit centrifuge will be an instrument that applies centrifugation technique to determine the ratio within the percentage of red blood cells and overall volume of blood. Now, if you ever think, why centrifuge blood? Here is your answer.
7, PRP Centrifuge
A PRP centrifuge machine has been taken into application by some of the leading specialists of Platelet-Rich-Plasma methods.
Centrifuge for PRP works for facial rejuvenation, plastic and facial surgery, veterinary applications and other sports injuries. These PRP centrifuges are available in large capacity as well as exceptional tube capacities.
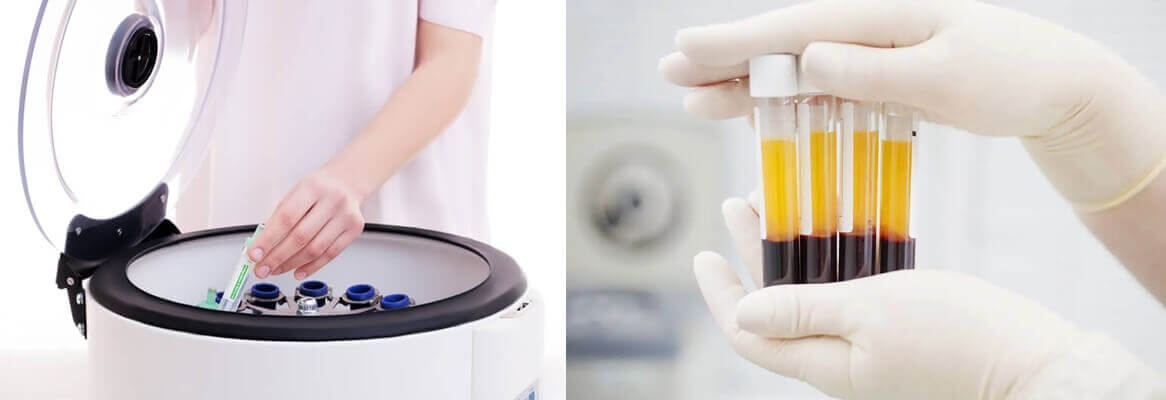
■ What Is PRP Centrifuge
The PRP centrifuge machines are specially designed to attain sufficient speeds to foster a centrifugal force to support a potent activity of completely separating the desired platelets from different blood cell types that consist of a certain percentage of plasma.
In simple terms, it is a centrifuge to separate plasma. PRP without centrifuge may cause issues as the tool supports the production of a completely saturated sample and has a higher composition of platelets.
It’s usually 5 to 10 times greater, as discovered in the unspun sample of the blood.
Suppose you search which centrifuge for PRP, then kindly choose 2400 rpm to 3600 rpm centrifuge speed for PRP procedure.
Once the saturated blood is extracted and separated, it is perfectly inserted in the position where the person has been afflicted.
8, High-Speed Centrifuge
High-speed centrifuges are one of the most versatile alternatives in the separation processing industry. This centrifuge lab equipment is taken into the application to deploy faster runs and enhanced control over the workflow.
With high-speed centrifuge rpm, one can handle massive amounts of samples. These could incorporate some tens of milliliters into a range of kilolitres.
Besides, a large centrifuge also can achieve greater angular velocities at a rate of approximately 30,000 rpm.
The rotors for these high-speed centrifuges would have a range of versatile adapters that supports several sizes of varying test tubes, microtiter plates and bottles.

Plen Medical High-Speed Centrifuges
■ High-Speed Centrifuge Definition
High-speed centrifuge rpm ranges within a greater rate of 15000 to 30,000 rpm. It is a super centrifuge usually seen in highly sophisticated laboratories that deal with biochemical application and demand a more excellent pace of operations.
■ High-Speed Centrifuge Principle
The high-speed centrifugal machine is equipped with a system that controls the specific procedure’s speed and temperature. It is highly crucial for the analysis of hazardous or delicate molecules.
These high-speed centrifuges have several adaptor options that help place the sample tubes of diverse volumes and sizes. Three of the rotor types are taken into application throughout the process.
9, Low-Speed Centrifuge
A low-speed centrifuge is observed to be used in general laboratory applications like biological sample separation related to blood, cellular materials, sperm and urine, among others.
A low-speed centrifuge is suitable for PRF, PRP, stem cell isolation, and lipid cell separation procedures.

If you want to buy a centrifuge for PRF, then a low-speed option would suffice your needs. Low-speed equipment is like a microplate centrifuge containing microbeads to cater soft and gentle spin-down to wash out cell lines and primary cells.
■ What Is a Low-Speed Centrifuge?
To understand low-speed centrifuges, one needs to know that they are mainly used to separate the particles. The maximum low-speed centrifuge rpm lies within a range of 4000 to 5000 rpm.
Their operation takes place within room temperature following the absence of control panels to monitor speed or temperature.
These are fixed-angle and swinging bucket rotor centrifuges, making them easy to use and compact in size.
Low-speed centrifuges machines can also be known as blood centrifuge machines as they suit accurate blood analysis and some other biological samples.
Though the working principle is the same as different high speed or average speed centrifuges, they are limited to simple solutions in terms of application.
10, Cytospin Centrifuge
Cytospin centrifuge is used to perform the method of cytospin. A cytospin can be acquired by deploying centrifugal force to concentrate, isolate and further discharge a single layer of cells from a diluted cell suspension on a circular base located on a slide.
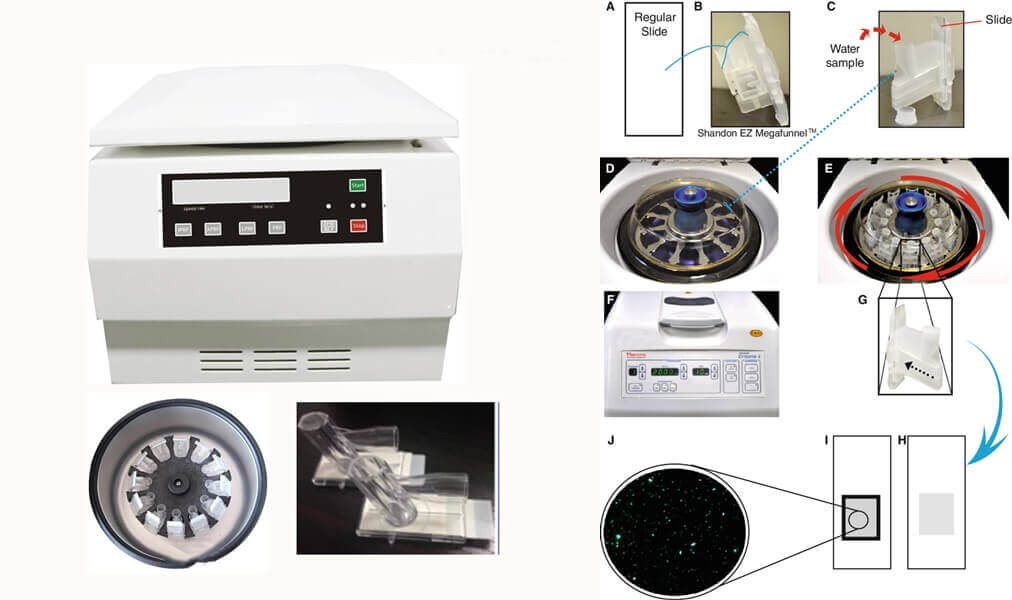

This method aims to ensure that cells stay intact so that their morphology could be conveniently examined. Shandon cytospin is one of the most famous centrifuges used in cytology, hematology and histology.
■ Cytospin Centrifuge Principle
The Shandon cytospin three works on the basic cytospin technique that performs a thin layer of preparation through cytocentrifugation fluids.
The Cytospin method is proper when an analysis of gynecological samples is required to be made.
It involves the deposition of the cellular monolayers on one slide to determine the pathological anatomy.
11, Gerber Centrifuge
A Gerber centrifuge is used in the Gerber method of extraction. This method is taken into the application to examine the fat composition in milk and is one of the most trusted globally.
The Gerber centrifuge machine is also known as the milk centrifuge machine that identifies the fat piece and further helps its extraction.
Centrifugation of milk is performed to execute various tests like fat determination, solubility determination and fat extraction.

■ What Is Gerber Centrifuge?
Gerber centrifuge is the product of a company called Gerber Instruments. It was established in 1892 and is famous for various instruments and analytical devices applied in the quality control sector of the dairy industry.
■ Gerber Centrifuge Principle
Gerber’s instrument is no less than a clinical centrifuge as it applies a volumetric method to perform fat separation from the milk using the centrifugal force.
The application of sulphuric acid is made to dissolve the protein which constitutes the membrane across the amyl alcohol and fat globules. It helps in the separation of fat from other solids.
12, Microcentrifuge
A micro-centrifuge machine is the most popular category of centrifuges mainly designed for microscopic samples in tubes with capacities like 5.0 ml.
One can find refrigerated microcentrifuge, high-speed microcentrifuge, mini microcentrifuge, and tabletop microcentrifuge categories with a tiny footprint than regular ones; hence, suit less-crowded areas of work.

■ Microcentrifuge Definition
A microcentrifuge can be referred to as laboratory equipment that works through a spinning mechanism.
This centrifuge can spin the liquid samples at substantially massive speeds. The types above of microcentrifuges are aligned with the sample’s size and capacity.
Varying microcentrifuges are suitable for diverse applications.
■ Microcentrifuge Working Principle
Microcentrifuge essentially uses centrifugal force to operate outwardly to affect the moving bodies in a circular motion.
One of the most distinctive features of this device is that no reasonable force is applied, and hence the centrifugal force could be assumed to be fictitious.
The outward motion comes into play through combined effect inertia as well as inward pushing external forces.
One could think that the centrifuge is to inertia as the wheel is to rotation. Rotation is quite crucial for centrifugation actually to come into practice.
13, Crude Oil Centrifuge
The use of a centrifuge to separate oil and water has also been one of the popular applications of the equipment. The crude oil centrifuge is usually applied to determine the percentage of sediment and moisture within the oil.
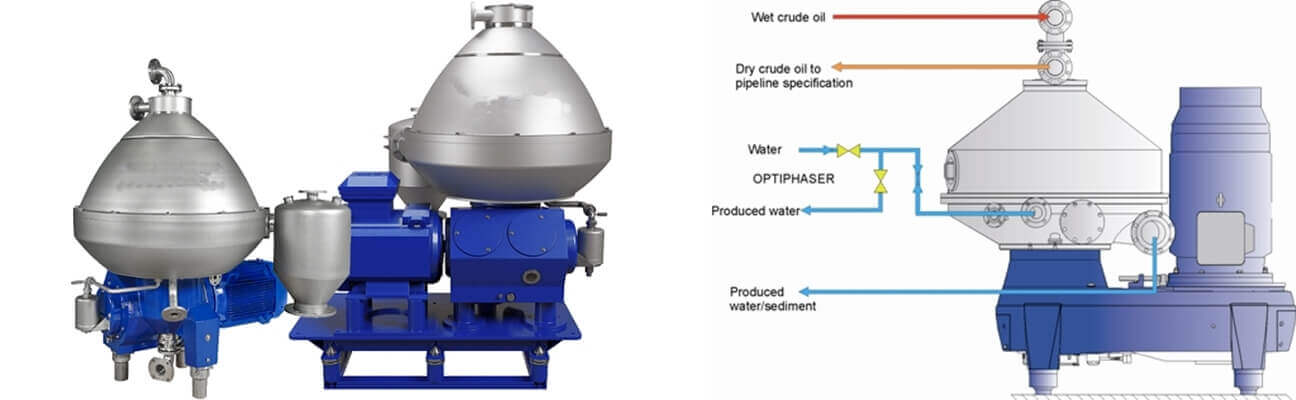

These centrifuge oil separators are reliable and even economical among oil cleaning technologies found within the industry. Usual oil filters persist with specific-sized holes within their mesh.
These are only helpful to remove particles through the oil stream that are not sized enough to pass through the hole.
Following the highly contaminated oil flow, such particles can turn into piles and further block the filter, further affecting the flow.
The waste oil centrifuge machine is not restricted through a pore size and hence, is capable of removing particles at sub-micron levels. The only possibility of these oil cleaning centrifuges is through the contamination or blockage of the rotors.
■ Oil Centrifuge Working Principle
The crude oil centrifuge machine incorporates circulation of the oil from the machine to the centrifuge through a dialysis system.
The rotor spins at an extensive speed of 7000 rpm. It further results in the gravitational force, which draws a specific particle in the external area while the refined oil goes back into the machinery.
To centrifuge oil and gas, it’s critical to ensure proper safety precautions.
The oil centrifuge is not just used in the primary crude oil and gas industry, but it also has micro-scale applications in the form of lube oil centrifuge, fuel centrifuge and engine oil centrifuge.
Besides, there are several manufacturers in the market offering oil centrifuges for sale.
14, Gel Card Centrifuge
Gel Card Centrifuge is another separation device applied in the processes like blood type routine tests, blood serology, microcolumn agglutination, erythrocyte washing, immunology and several other types of tests.
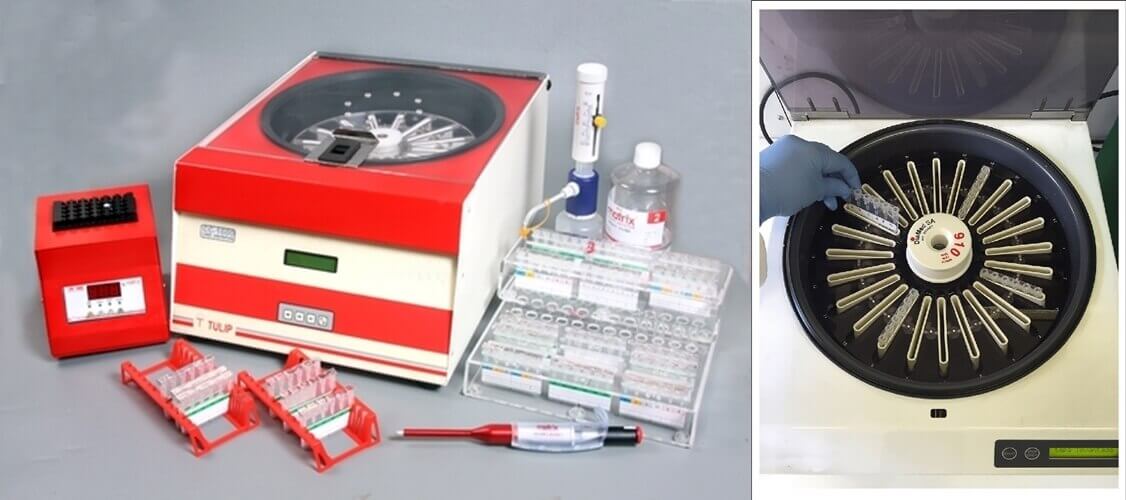
This centrifugation filtration technique is compatible with three of the rotor types. Centrifuge can be equipped with three rotors, out of which one can be used for serology testing and can consist of 10 to 13 mm culture tubes.
The other rotors are particularly for gel cards that will be applied in the screening of antibodies. The last of the rotors are specifically designed for the washing of lymphocytes.
These are blood bank centrifuges as they work for several manual testing.
Although, one needs to make sure before moving towards a centrifuge price decision. Some of their variants are also suitable for industrial decanter usage.
■ Gel Card Centrifuge Principle
The gel card centrifugation works with control over the molecular sieve pore. It takes place as the types of gels are consistently changed as per varying concentrations.
In this process, the molecular sieve ensures that only free red blood cells should pass.
Hence, it becomes successful in resolving agglutination of non-agglutinating erythrocytes and red blood cells. Centrifuge speed and time for blood are essential to be accurate in this process.
15, RCF Centrifuge
While exploring centrifuge, you must have come across the term RCF.
Well, if you think what is the difference between RPM, RCF and g. RPM, as you know, is Rate Per Minute, RCF, on the other hand, is a Relative centrifugal field, and g is the abbreviation given to earth’s gravitational field.
Before the difference, you need to know the similarity. The similarity is g, RPM or RCF are the units to measure the strength of the centrifugal field in varying departments.
RCF reflects and compares the field’s power generated from varying rotor sizes and operational speeds.
■ RCF Centrifuge Definition
The g-force or RCF defines the sample object’s gravitational force. One can assume it to be centrifuge 10000 rpm as in the spinning rate or 10000 g centrifuge as the strength of the gravitational field.
On the part of RCF, it considers the speed of the rotation as it evaluates the distance between the rotation’s center to define the g-measurement. If you ever wonder which centrifuge is used for which process, then the answer could be broad.
However, when it comes to the method that measures centrifugation strength, RCF is the ideal method as it remains constant across industries and rotor types and sizes.
16, Laboratory Centrifuge
Many people wonder if a usual centrifuge suffices various laboratory uses, so who uses laboratory centrifuge or why to use such specific equipment. A laboratory centrifuge is required in the particular operation due to its speed.
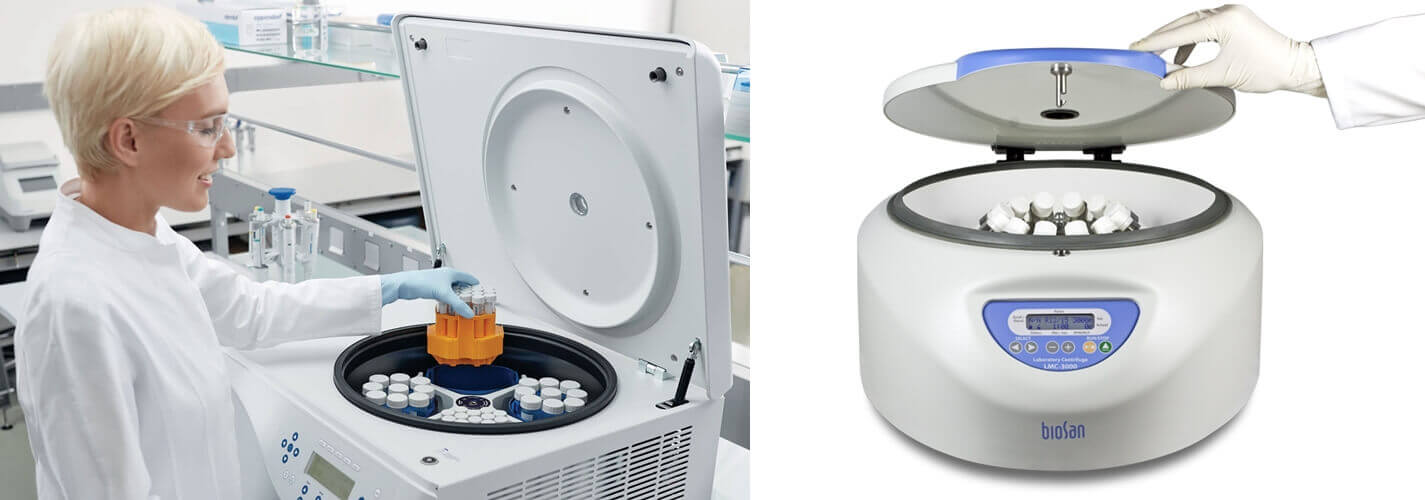

Such perfect rotation of the centrifuge accelerates centripetal movement and further proffers the separation process as per the density of the substance.
This type of centrifuge caters to varying applications, especially in the research laboratory, hospital sections and other clinical facilities.
The factors that affect the variation within these laboratory centrifuges include sample size, refrigeration capacity, optical identification capability and rotor velocity.
Apart from laboratory centrifuge price, the purchase considerations incorporate noise, rotor type, model versatility and corrosion resistance.
■ Laboratory Centrifuge Definition
A simple definition of laboratory centrifuge would define it as an electric centrifuge that can spin liquid samples at a substantially higher pace. It aids the extraction of suspended materials from the given medium.
The use of a centrifuge with blood can be seen in separating serum or plasma from the blood samples.
17, Centrifuge Veterinary
A centrifuge is used during animal experiments to develop differences within the fluid’s liquid as per their density. It incorporates methods like density gradient centrifugation of DNA, which requires extensive speed of spinning.

Not just DNA, but veterinary centrifugation is also helpful in separating hematocrit, blood, urine and other routine samples. One of the options available in the market is of automated centrifuge that separates pieces within a fraction of time.
What are the functions of different types of centrifuges?
Centrifuge can be used for several research and laboratory purposes. Centrifuge for blood samples has several functions in the clinical as well as medical research laboratories. They purify organelle, cells, nucleic acid, viruses and proteins.
Some of the parts align with:
1, Clinical Centrifuge Function: One of the functions is the centrifugation of whole blood to extract several components of blood separately.
Varying evaluations require plasma or serum that can be achieved through the principles of centrifugation in chemistry.
You can obtain serum when you centrifuge the whole blood sample clot at room temperature. The process removes the chunk while only the serum remains.
If you ever think about what centrifuge tubes are used for, their application in plasma extraction is of utmost importance.
The whole blood sample is collected without letting it be a clot. This is why centrifuge blood samples in this technique are equipped with serum and plasma altogether.
The entire blood sample is gathered within the tubes and is further treated along with anticoagulants. It’s further sent for centrifugation to collect plasma supernatant and further extract the cells.
2, Refrigerated Centrifuge Function: This type of centrifuges is taken into use for samples that demand a specific temperature range.
The function requires them to work at a maximum speed while maintaining the level of temperature.
It is suitable for centrifuge DNA, PCR, RNA and varying antibodies. They are also known as medical centrifuges, following their extensive function in the health care areas.
3, Microhematocrit Centrifuge Function: Micro hematocrit centrifuge is used to determine the volume fractions of erythrocyte within the blood to pursue the separation of micro volumes within liquids, solutions, and blood.
Its function is related to blood bag centrifuge as it works for biochemistry, blood separation, and immunity genetics while pursuing clinical tests.
Some of the parts or applications are related to the diagnosis of polycythemia, bone marrow failure, anemia, multiple myeloma, and leukemia.
Micro hematocrit centrifuges are also known as capillary centrifuges due to their use of microcapillary tubes to hold the sample.
4, Blood Centrifuge Function: This centrifuge applies a centrifugal force to draw separation within the varying blood components in definite layers.
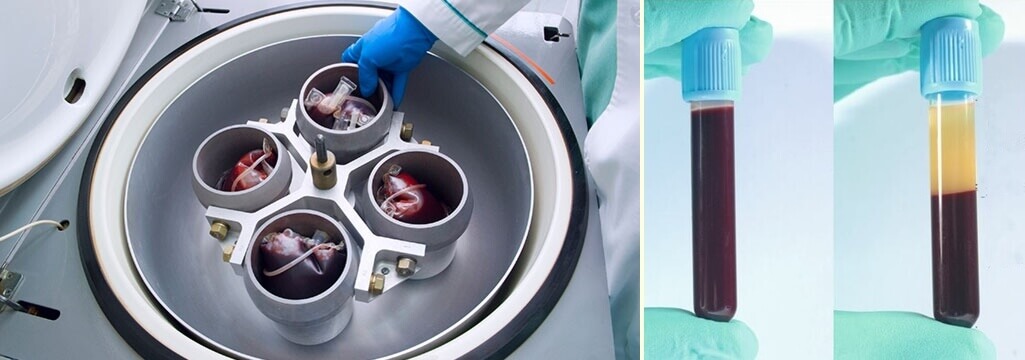
If you plan to buy a blood centrifuge, it is critical to know what centrifuge speed to separate blood should be applied.
Though for plasma, a high speed is not necessary, but at least 2200 to 2500 rpm is critical with 15 minutes.
5, Centrifuge Swing Out Rotor Function: Swing-out rotor is a bucket centrifuge that incorporates specific tubes that are not rigid and attached to a particular angle.
The alignment of the buckets is pursued in a way where it enables the spin in the horizontal direction.
Such a rotor is specifically used when density gradient centrifugation is taken into consideration.
With the help of a longer path length, the mixer centrifuge could achieve enhanced separation. Although, such a rotor doesn’t aid the purpose of pelleting.
6, Mini Centrifuge Function: Mini centrifuge’s function is similar to the floor and benchtop one.
They are used in several industries like molecular biology, environment, chemical and other areas of medical research. Accurately designed for a spin-down centrifuge motion, they are commercially viable.
What’s the price of different types of centrifuges?
-
How Much Does A Centrifuge Cost?
The variety of centrifuges is wide. An average centrifuge cost varies per brand, type, style, model, speed and many more factors.
A centrifuge machine cost would broadly vary within a price range of $1000 to $50,000 on an average. This range can go up as well.
A centrifuge machine’s price varies a lot on the type and its usage. For instance, a centrifuge price for a laboratory would differ from a specific PRP machine price.
- PRP Machine Price: The PRP centrifuge machine price will be different as per the brand; however, as of Amazon.com, centrifuge for PRP prices vary within a range starting from $350. Whenever you look for a PRP centrifuge machine for sale, check all the parameters before deciding.
- Refrigerated Centrifuge Price: Such a centrifuge machine cost would be around $ 1000 to $2000. One of the models available on amazon had a price of $1602.59.
- Industrial Centrifuge Machine Price: Industrial centrifuge machine prices can be on the high end of the market. It starts from $5000 and can go up to $50,000.
- Laboratory Centrifuge Machine Price: If you check laboratory centrifuge machines for sale, the cost can go up to $25000.
- Benchtop Centrifuge Price: These centrifuges’ cost varies within a range of $1000 to $5000.
- Microcentrifuge Price: A microcentrifuge price varies within a range of $500 to $2500.
- Decanter Centrifuge Cost: Decanter centrifuge cost depends on the decanter centrifuge manufacturer and the capacity and size of the equipment. If you buy a new centrifuge, the cost would be around $50,000 for a small degree. The cost of a giant centrifuge will be $1 million.
- Blood Centrifuge Machine Price: The cost starts with $250 for such a clinical centrifuge.
- Mini Centrifuge Price: The price range of a mini centrifuge is within $28 to a massive high end of $63 112.
- High-Speed Centrifuge Price: High-speed centrifuge price varies within a range of $10,000 to $25000.
- Gerber Centrifuge Machine Price: The cost of a Gerber milk separator is around $450, as mentioned on Amazon.com.
How To Choose Centrifuges?

1, Flexibility is key
A centrifuge is used for separation tasks in various industries. This means that one machine may or may not have multiple users.
Therefore, before you start opting for the ‘centrifuge rental near me’ option, assess your business’s present and future requirements.
2, RPMs are essential, but G-Force is even better.
Overall, rpm and g play an essential role in the machine’s functioning. While the traditional instruments followed RPM, the recent models are designed with the finest G-Force.
So, before you think about which centrifuge is balanced correctly, consider estimating the G-Force the prospective samples may need. This will help you make a better selection for the company.
3, Factor in available space in your lab
There are different sizes and types of centrifuges in pharma and other industries. The choice varies based on the industry or business you are in.
So check whether you need a small centrifuge machine or a large water centrifuge. The available floor space will determine this factor. Handy desktop centrifuge versions are also available.
4, Make life easy on yourself and your labmates.
A quick spin centrifuge can help you save lots of time in the initial separation process. The staff and operators will find using these handy devices very easy as most new models have a user-friendly control panel.
5, Speed
The first factor that you should consider before you think- ‘Where can I buy a centrifuge?’, is to see what speed your samples require.
However, while focusing on the RPMs, do not overlook the RCF (Relative Centrifugal Force). It determines the force exerted on rotor components and, hence, is very important.
6, Temperature
Most commercial centrifuge operates at average room temperatures. They do not come with heating or cooling options. But, there are a few cooling centrifuge options that can also be considered. They operate in lower temperatures like -10°C or -20°C.
7, Capacity
A high capacity centrifuge is a popular pick of industries or businesses that deal in large-scale production. However, consider a lower centrifuge capacity that caters to your requirements if you are looking for a more effective and sustainable alternative.
8, Centrifuge Rotor
There are different rotor types, including fixed angle, swinging bucket, etc., discussed in the sections below. There are also options like PCR strip, vertical, and micro-plate. Therefore, before you pick one centrifuge to buy, check its rotor type.
























