Plen Medical-Laboratory Centrifuge Machine Center
Your Reliable laboratory Centrifuge Manufacturers in China
While they are highly functional devices, what centrifuge is used for? One of the most common uses of Centrifuges is Pelleting.
In this process, the particles of a sample are separated and gather like a pellet on the tube base. This collected substance is called supernatant.
Furthermore, during this process, the chemicals turn from an aqueous or matrix solution to a solvent.
While in Ultrafiltration, the operator uses a membrane to purify, isolate, and concentrate macromolecules.
The isodensity gradient centrifugation was further carried out by the autogenous method formed by equilibrium sedimentation.
Can I use the centrifuge at home?
Surely you can. You can choose Benchtop Microcentrifuges, small size but got all functions of a laboratory centrifuge for home use.
Please get in touch with us and tell us which samples you will separate, then we will give you a tailor-made recommendation.
What precautions should I take while using a centrifuge?
What type of centrifuge is used for blood?
We usually use Benchtop & low-speed centrifuges to separate blood components such as serum, plasma, platelets, red blood cells, etc.
Will centrifuge noisy?
If you balance it properly, it’s hushed. The noise dB(A) ≤ 58 dB(A). If the centrifuge you got is very noisy, please check whether you have balanced the centrifuges well or not.
How is a centrifuge balanced?
It’s effortless. The rotor is similar to a balance; samples with the same weight must be placed on the exact opposite side of the rotor, that is, on the same line through the center.
A machine that deploys controlled centrifugal force, the force generated from rotation, is called a Centrifuge. The device provides the best substitution for the solid gravitational force.
Every centrifuge machine has a robust spinning vessel that comes in different configurations based on its application.

Its application and functioning are very similar to a rotating drum of a laundry machine. The drum is used to remove excess water from the clothes.
The centrifuge is the industrial version of this device to separate fluids from a crushed solid matter.
Centrifuge signifies a device that rotates at a very high speed and separates different substances, with varying densities, by centrifugal force.
The crucial position and use of centrifuge in the laboratory have made it irreplaceable equipment in the industry.
A centrifuge is used to separate samples, for instance, pelleting proteins or nucleic acids from a solution or performing microfiltration for smaller aqueous pieces.
The process allows the liquid to collect at the bottom of the test tube to prevent any wastage.
Using these makes substance separation quick and straightforward for professionals who work in laboratories. One does not need assistance from a technician to complete the process.
Biological centrifugation is the process that employs centrifugal force to divide solutions of biological particles. Offering separated liquid components purifies the initial mixture.
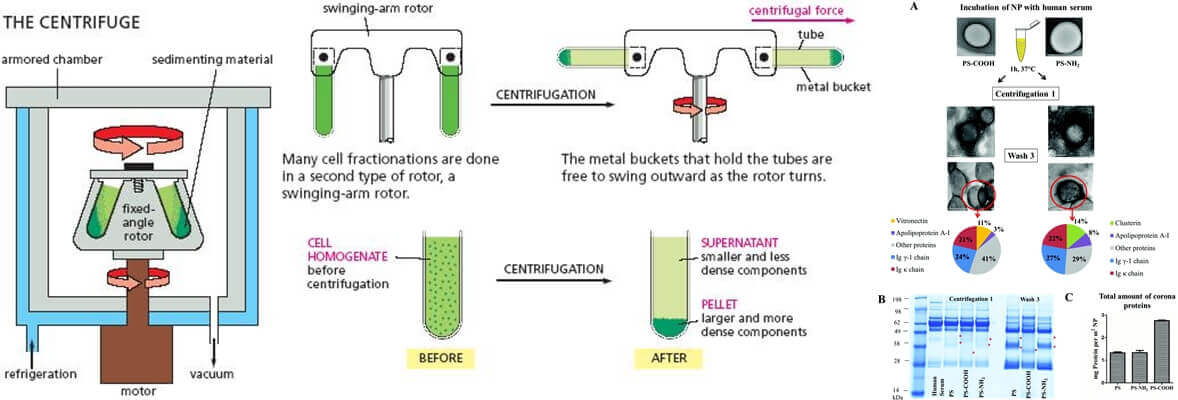
In biology, centrifugal separation is an important technology for analyzing and separating supramolecular complexes, subcellular components, macromolecules, and other cells or molecules.
This is a common approach in the industry and is used extensively in biological laboratories.
Centrifugation can also be used for DNA Precipitation, gathering cells, observing molecular conformation differences, and purifying virus particles.
Centrifugation is a mechanical procedure that uses the density or particle size of the mixture and exerts centrifugal force to foster easy separation of different elements.
The principles that simulate the behavior of particles during this process can be discerned instinctively.
In a laboratory, a Centrifuge is used as a separation method to isolate particles of a solution.
This can be done based on the density, shape, size, and consistency of the component with varying rotor speeds. Particles are infused in a liquid medium before being placed in a centrifuge tube.
Later, the tubes are taken and secured in a centrifuge rotor, and the process is followed by spinning the solution at a defined speed.
While separation can also be done by employing Earth’s natural gravitational pull, it is a time-consuming approach.
Centrifugation just speeds up the process as the rotor’s spinning generates a considerable amount of centrifugal force, which aids in quicker separation.
Industrial Centrifuge Machine is also one of the most essential and fundamental lab instruments. This is mainly because it provides efficient preparation and isolation of particles from samples with different viscosities.

Over the years, the use of Centrifuge machines has increased significantly. But, when was centrifuge invented?
Even though it has gained popularity recently, the device has been in existence for centuries. As for when was centrifuge discovered? One of the earliest appearances made by the machine is in the 1400s in hand-powered milk separators.
With the mainly medical and scientific application, the first commercialized design of a Centrifuge was launched in the 1800s.
The next question that pops up in your mind would be; who invented the centrifuge machine? Back in 1864, the first model of Centrifuge-style device was designed by Antonin Prandtl.
Operated by hand, a centrifuge machine was used to separate cream from milk at an industrial level in the dairy sector. After him, a Swiss Biologist & Physician, Friedrich Miescher, became the first person to use these in a laboratory setting.
In 1869, he started using a basic centrifuge system to isolate nucleic acids from WBC nuclei. This became a significant milestone in DNA Inheritance-based studies and research.
Miescher’s achievements gained popularity in the domain, which also inspired the development of initial models of continuous Centrifuge Sep0arator.
These were made by Gustaf De Laval in 1879 and were initially used as an Impulse Steam Turbine.
Following De Laval’s notions, the industry witnessed a boom in laboratory centrifuge machine commercialization. Since then, they have been used in manufacturing contemporary dairy industrial machines and rocket engines.
Furthermore, the growing demands for high-speed machinery became Theodor Svedberg’s motivation.
In 1925, this Colloid Chemist made some updates to the original lab centrifuge machine and used the new Ultracentrifuge device as an analytical tool.
After a year, Svedberg was awarded a Nobel Prize for his invention and research. The chemist aimed to employ a centrifuge machine to isolate macromolecules, which usually need a high speed of 1,000,000 x g.
By 1930, Albert Claude, a Belgian Cell Biologist and Doctor, uncovered the Cell Fractionation process, in which Centrifuge Extraction plays an important role.
In the following decades, especially the 1950s, numerous revolutionary discoveries and inventions were made in the Centrifuga Laboratorio field.
In 1942, a paper titled- ‘Albert Claude published isolation of Chromatin Threads from the resting Nucleus of Leukemic Cells’ with James S. Potter.
This report stated that the duo was successful in extracting Chromatin Threads by following continuous centrifuge separation steps.
The samples taken underwent centrifugation till the required cell component was obtained, or they reached supernatant.
In the post-WW2 period, around 1946-47, Jesse Beams’ apprentice- Edward Pickles-started Spinco. The company dealt with designing and manufacturing Ultracentrifuges.
They released their first variant- Model L, in 1949, which is said to provide a centrifuge speed of 40,000 rpm.
Over the next few years, Centrifuge with Rotors was made from newer materials to increase their durability and functionality.
For floor-standing centrifuge, innovative Fiberlite TM Carbon Fiber Rotors were used in Thermo ScientificTM portfolios.
At present, options like a tabletop centrifuge, floor centrifuge, and industrial centrifuge are also available. Selection can be made based on the requirements and applications of the device.
If you are still wondering- “How centrifuge works in separation?” then this section will provide you with a satisfactory answer.
A Centrifuge operates on the theory of sedimentation. When enacted upon by gravity, the substances in a solution react based on their viscosity. There are five main types of separation, namely:
Density Centrifugation will gradually separate the components with even the slightest difference in their density. The following factors influence the process:
The Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF), which is also referred to as G-Force, is the total acceleration exerted on the sample.
When frictional forces or buoyant become lesser than RCF, the particles start moving away from the rotational axis. This results in proper sedimentation of the mixture.
Have questions about the centrifuge and its parts? Then remember Electrical Motor and Rotor Assembly are the two main parts of any lab Centrifuge Machine.
Its components and their functions are explained below:

This is the component that is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
As a result, it generates a rotational motion in the device. A conventional mini centrifuge machine is powered by a motor that produces 100W and 150W power.
Located in the Rotor Assembly are centrifuge tubes consisting of Drive Shaft and Tube Holders. It takes the energy produced by the motor and carries it to the application point.
This part is accountable for transferring the rotation motion from the engine. There are three different centrifuge rotor types:

The Centrifuges generally have a dynamic compressor or turbocompressor. Featuring a radial design, these draw in air to the center of the impeller.
The rotating impeller has blades spread out, which helps push the attitude towards the center by using centrifugal force.
This movement generates pressure increase and results in the formation of Kinetic energy.
Wondering how a centrifuge machine works? The process is quite simple; the centrifuge machine uses an accelerated rotating motion to replicate the effect of gravity. As a result, different particles of a mixture get separated easily.
Keeping the forces involved in mind, the portable centrifuge machine is designed skillfully to ensure operator safety.
For every sample, gravity acts to separate the particles based on their density. This means that components with high density are prone to sink, leaving elements with lower density to float on the top.
The centrifuge uses the tiniest of differences in the particle viscosity to aid quicker separation within the mixture.
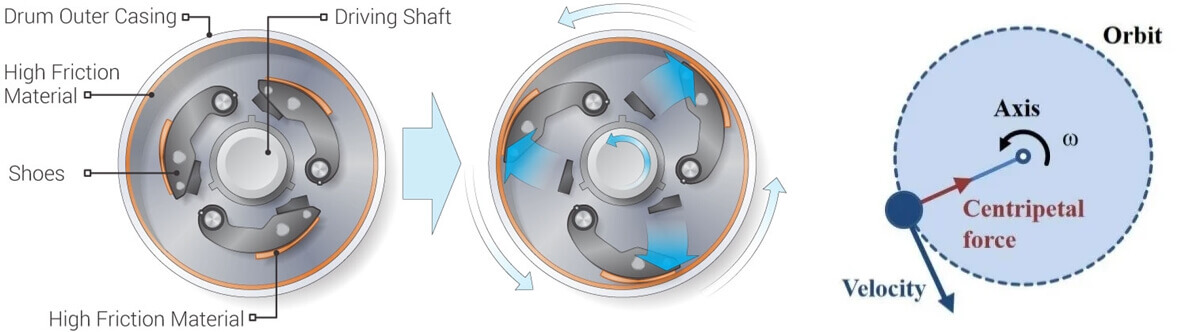
While the rotor continues spinning on its axis, the centrifugal force pressures the particles in the sample to move away from the rotational axis.
Furthermore, increased centrifugal force may also assist in sedimentation if it surpasses the buoyancy of the solution and friction created by dissolved particles.
Now, it is time to review centrifuge vs. serfage. Like a centrifuge, a Serological Centrifuge is another lab tool commonly used in the blood banking industry.
The instrument spins to separate the serum from the blood cells.
At the same time, the normal centrifuges are employed for grading and washing of Red Blood Cells. The recommended blood centrifuge speed is between 3400rpm and 3500rpm.
Understanding why centrifuge is used in the industry can be a little tricky for a few people.
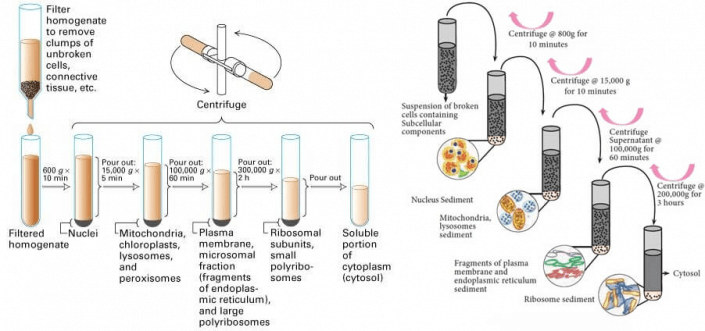
The Ultracentrifuge or Centrifuge time and speed are maintained to provide optimal molecular or atomic isotope separation. The isolation of isotopes is usually performed during scientific research to produce nuclear weapons or fuel.
In general, the centrifuge can be used for liquid & solid separation, also being the most typical application.
However, rather than obtaining pure drinks, the separated particles can also be used to create gases. Moreover, they are also used for other mechanical separations.
How to use a centrifuge in a laboratory? Under lab environments, a high rpm centrifuge with larger sizes is used. Depending on its requirement, a small centrifuge and large capacity centrifuge are employed for the task.
A portable centrifuge is also used, as they cover less space on the counters and can be carried along easily. Since the sample tubes are secured at a particular angle, the separation can be performed relatively quickly.
Furthermore, most labs use fixed angle rotor centrifuge, but a centrifuge with a swinging bucket rotor is also a popular choice. These are typically used to isolate DNA, blood components, and chemical purification.

Now, where is centrifuge found in most homes? For regular uses, the operators prefer using medium-sized centrifuges. It does not only provide quick separation but is also easy to store and use.
Centrifugation in the washing machine is one of the best examples of finding applications of similar processes.
The devices have a dryer feature, which separates the water from cleaned clothes. Salad spinners are another example of finding centrifugation in daily life functions.
Tubular Bowl Centrifuge is used in the food industry. It has a vertical cylinder placed in a stationary case and can rotate at a speed of 15,000 to 50,000rpm. This instrument is used to separate immiscible liquids, for instance, water and vegetable oil mixture.

The solution’s components will be divided into annular layers, in which the denser part will settle close to the bowel wall. A tubular centrifuge is used mainly because it delivers better liquid separation.
Centrifuges are also available in industrial models used to separate bulk samples, mainly colloid components.
It is also used in removing solids from drilling fluids, chemical preparations, removing sludge during water treatment, and even while drying minerals.
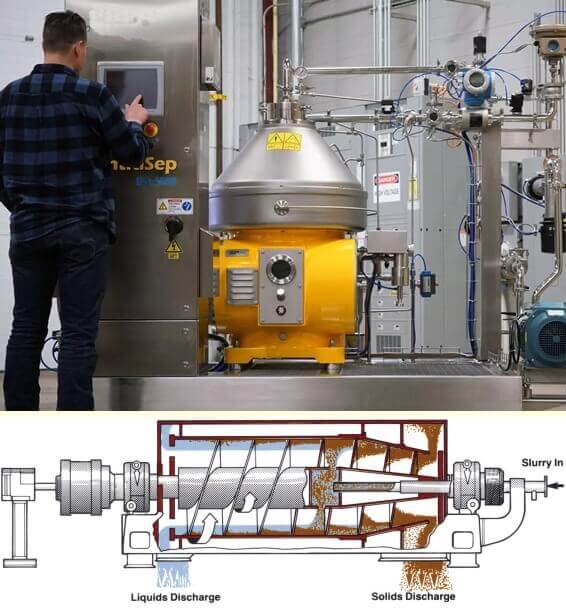

Few industrial centrifuges follow structured separation methods, while others use a filter or screen to provide isolation. They are also used for casting metals.
However, the properties and composition of the material affect the differential gravity, which alters the outcomes.
Speed plays a vital role in providing accurate separation as it uses particle density to isolate it from the other components.
However, another question that arises is why centrifuge samples need varying speeds?
Apart from being categorized based on their making and design, Centrifugation devices are also classified according to their maximum speed.
In these groups, the centrifuges with 0-7,500 rpm speed are considered to be low-speed.
While the speed increases to 20,000 rpm and more for further groupings, in a Centrifuge, RCF is used to denote the rotor speed in terms of gravity (x g) for many procedures.
While a few states are the same in RPM, this helps the researchers ensure optimal experimental conditions.
Generally, the advised speed for a centrifuge to separate blood is 3500 rpm. For chemistry testing, the sample should spin for at least 10 minutes in the instrument.
But for coagulation tests, the model should be left for only 7 minutes.
The recommended cell centrifuge speed is 1036 rpm, i.e., 180 x g, only if the apparatus has a 15cm radius.
Confused about how a centrifuge works on blood samples? Then read this section to find out. In the case where serum gel separator tube is not being used, follow the below-listed steps to acquire plasma:
The steps to use a centrifuge in laboratory conditions are:
Using a Centrifuge device is very simple. You will have to start by checking whether the centrifuge is functioning correctly.
The instrument should be accurately serviced and calibrated by the authorized service center or directly the centrifuge manufacturer.
You may use a Tachometer to keep track of the rotor speed. Few other points to remember are:
1, Ensure the centrifuge is placed on a plain surface and has a firm footing on the base.
2, Always check the tube balance before running the machine. Having an unbalanced batch can cause considerable damage to the samples.
It can also break the test tubes and cause the centrifuge to wobble, even on a stable surface.
This will affect its performance and longevity. As mentioned above, add a substitution tube on the holder side that has fewer sample tubes.
3, If the machine is still shaking or wobbling when used, switch it off and pull out the plug. Troubleshoot the device and check whether the sample load was balanced correctly.
Furthermore, if the machine uses an adaptor, check its placement as well.
If the problem continues, you will have to remove the rotor to check for glass shards or debris deposition that is not hindering its movement.
The last option, after this, would be to send it for proper repair to the manufacturer or service center.
4, Always check that the rotor has come to a complete stop before you open the lid. While a few latest models come with safety locks, the traditional or older versions don’t have the same feature.
Opening the top when the rotor is in motion can cause damage to the samples and also result in physical injuries for the operator.
5, Handle the samples while wearing gloves and goggles for optimal protection against any causality. Furthermore, if handling chemical solutions, it is advised that the operator wears a face shield.
This will safeguard them against potential burns. Having safety gear on will also protect you in case of equipment failures.
5, Check the placement of the centrifuge. It should not bump or touch anything, especially when it’s running. Keep the plug cord out of reach to avoid tripping or other accidents.
While performing a complete Centrifuge repair, one has to keep numerous factors in mind. While you can get professional assistance, if you just need a quick clean-up, then follow these measures:
Follow these steps, and you can avoid facing sudden centrifuge breakdowns between essential operations. If you feel overwhelmed, just search for centrifuge repair near me to get the best providers.

The adept service agents will reach your instrument up and running in no time. They will also ensure that the tool is delivering equally compelling performance.

Keeping the design perspective, the continuous centrifuge is constructed by putting together multiple moving parts. These components interact with low tolerance. Thus, to maintain the tool’s durability, you will have to find the faulting area.
Centrifuges, like other machines, require periodic inspections to run smoothly. If you wish to maintain its performance, check the centrifuge’s working in its pre, during, and post-use stages.
For a digital centrifuge machine, one can easily view the ‘one key’ warning, which indicates the presence of a foreign or oily substance.
Every time you use the centrifuge, check for any unusual air exhaust, shaking, discharge, or speed. While the problem can be anything, identifying these initial stage symptoms can help avoid significant faults and minimize the damage.

To lower the chances of facing any machine failure, perform regular lubrication and clean-up of the instrument.
Make sure you remove any unwanted substance or debris from the machinery. Furthermore, use only the manufacturer-advised products to clean the tool.
If the operators are committed to taking proper machine maintenance measures, you can ensure a safer work culture.
This can help you sustain optimal centrifugation time, speed, and performance. Following regular maintenance routines can also improve centrifuge instrument output.

To get the best cleaning, try these:
For Swinging Bucket, you will have to follow additional rotor maintenance steps:
For Fixed Angle, follow these maintenance steps:
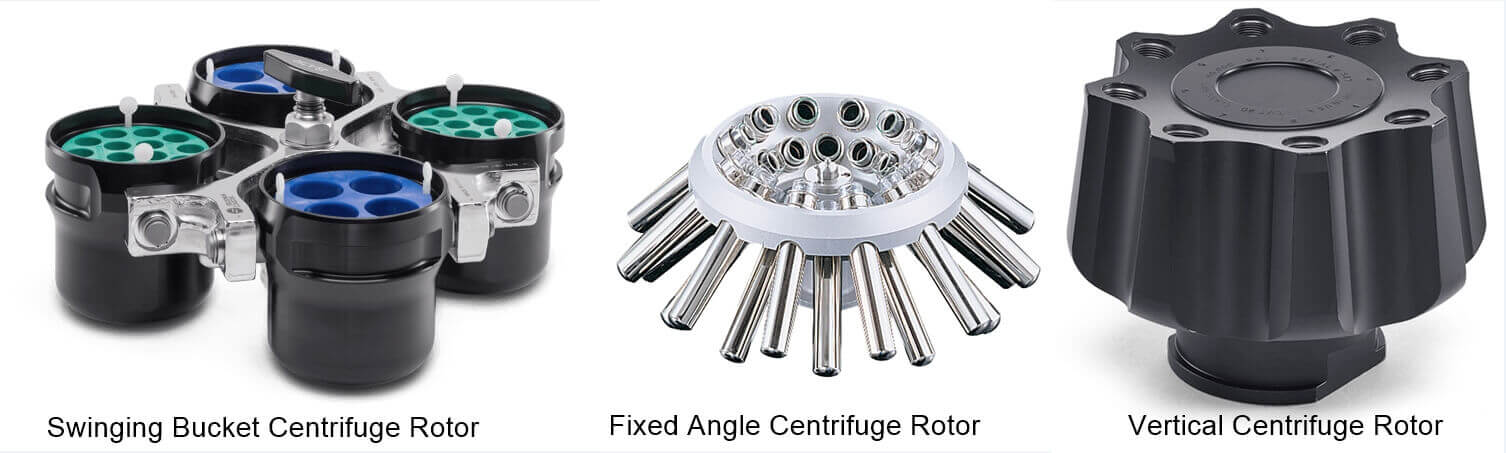
There are three main types of rotors:
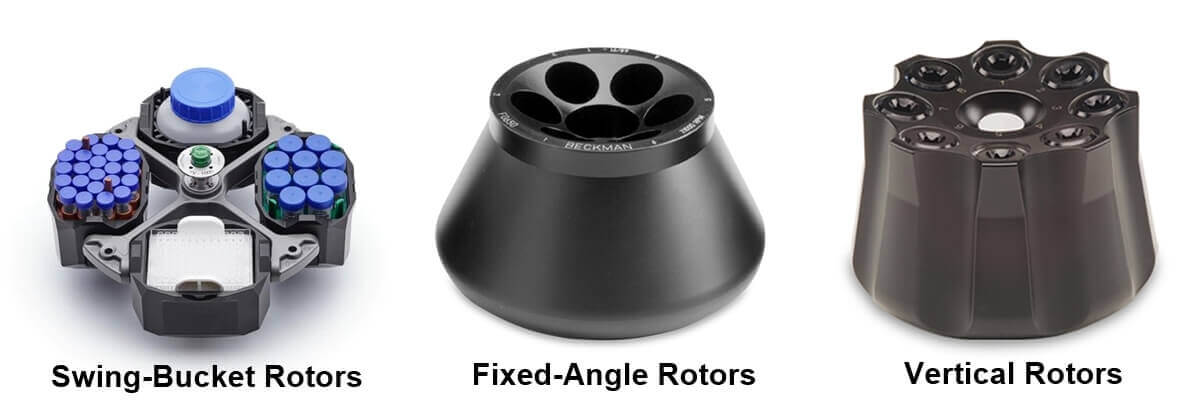

These are designed to cater to 3 particular factors- Volume Range, Centrifugation Type, and Speed. The first two names in the list are some of the most commonly used rotors.
Applications that need benchtop centrifuge or high/low-speed centrifuge require these types.
On the contrary, vertical types are fundamentally used in ultracentrifugation. Fabricated from titanium, carbon fiber, aluminum, etc., the material choice depends on the application of the rotor.
A quick introduction to all the rotor types mentioned above:
These rotors are generally used to separate samples with 36 mL to 2.2 mL volume. Ideal for both Isopycnic and Rate-Zonal centrifugation processes.
However, the best results are obtained from rate-zonal separations.
The rotor types are primarily used in Pelleting. Whether you have to collect pellets or remove debris, this is the best rotor option for you.
These can efficiently work with 0.2 mL to 1 mL samples.
These are highly specialized rotors. They are used explicitly for DNA banding with cesium chloride. With lower K factors, the run time for these is relatively short as well.
Every component of a mixture has its unique physical properties. These geological characteristics make it different from other items and aids in the isolation process.
CSCL Density Gradient centrifugation focuses on two aspects, being density and size.
The size of the particles determines the duration required to achieve complete separation.
An unbalanced centrifuge can be discerned by its swift rotor movement and production of extreme forces.
Therefore, to ensure the longevity of the machine and rotors, it is essential to keep the test tubes balanced.

Furthermore, maintaining the right balance becomes even more critical for the operator when the batch undergoes high-speed centrifugation.
Loading test tubes with incorrect quantities of samples can cause permanent damage to the instrument’s mechanics.
An imbalance in the loading can also damage the solutions and injure the operator. In worst scenarios, the unbalanced batch loading can cause a rotor crash.
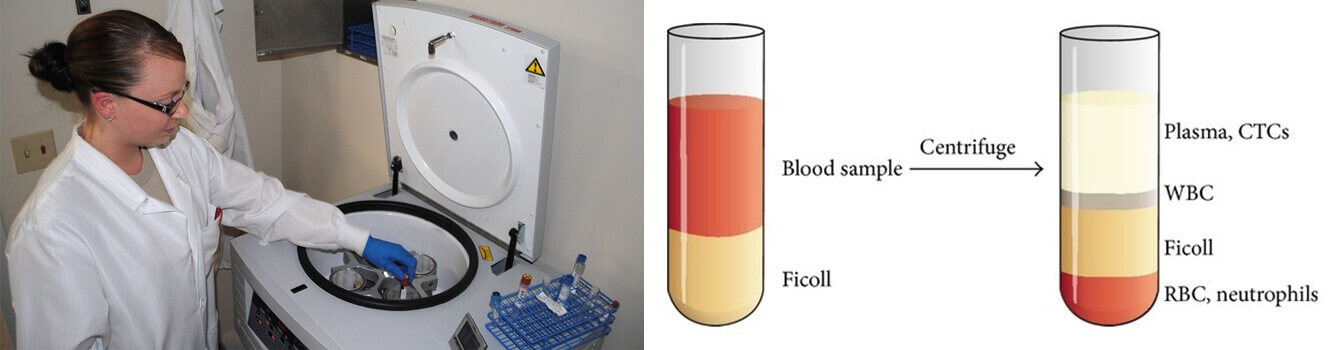
The centrifuge and Blood Component separation process go hand in hand. Using this device, the operators isolate blood components like plasma, RBCs, and platelets from each other.
The resulting tube has precipitate layers of different particles.
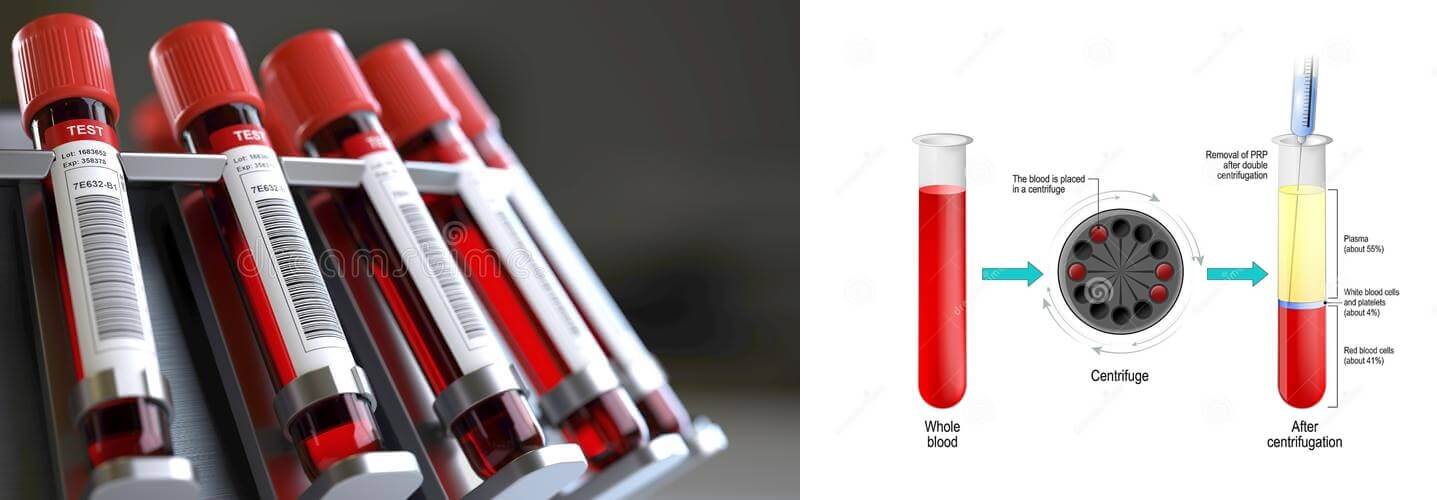

In medical science, blood samples are collected in clean test tubes or vials with different capacities. This is the first step in blood plasma separation, blood cell separation, and almost all similar processes.
Generally, for these, the operators prefer using fixed angle and swing-out rotors.
These rotor types allow the components to gather on the bottom of the tube, forming an even layer. It delivers quicker separation for further testing.
Laboratories should never perform centrifugation instantly after drawing the blood from the patient. They should wait at least 30 minutes to let the blood clot. However, do not exceed the 60 min limit for running centrifugation.
Set the device for 2200-2500 RPM and allow the sample to spin for 15 minutes minimum.
In Centrifugal separation, the substances of a particular sample are isolated by exerting specific gravitational forces.
The process uses centrifugal force and is also called Cyclones. They majorly rely on inertial forces while moving in a curvilinear direction.
By this process, particles get deposited on the outside wall of the tubes. But, the efficient collection of isolated particles depends on the inlet’s airflow, particle size, speed of spinning, and collector dimension.
It is noted that with particles of size 10-μm diameter and more prominent, the efficiency rates for this process increase up to 90%.